4 Examples Of Solids: Understanding The Properties And Types
When we think about solids, we often envision objects that maintain their shape and volume, unlike liquids or gases. In this article, we will explore four examples of solids that illustrate various properties and classifications within this state of matter. Solids are defined by their structural rigidity and resistance to changes in shape and volume. This article will delve into the characteristics of solids, providing a comprehensive understanding of their nature and significance. By examining specific examples, we can appreciate the diversity and applications of solid materials in our daily lives.
Understanding solids is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for practical applications in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and technology. The study of solids encompasses various fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering. By the end of this article, readers will gain insights into the fundamental properties of solids and their relevance in both natural and engineered environments.
Let’s embark on this journey to discover the fascinating world of solids, starting with a closer look at four specific examples that highlight their unique characteristics and applications.
Table of Contents
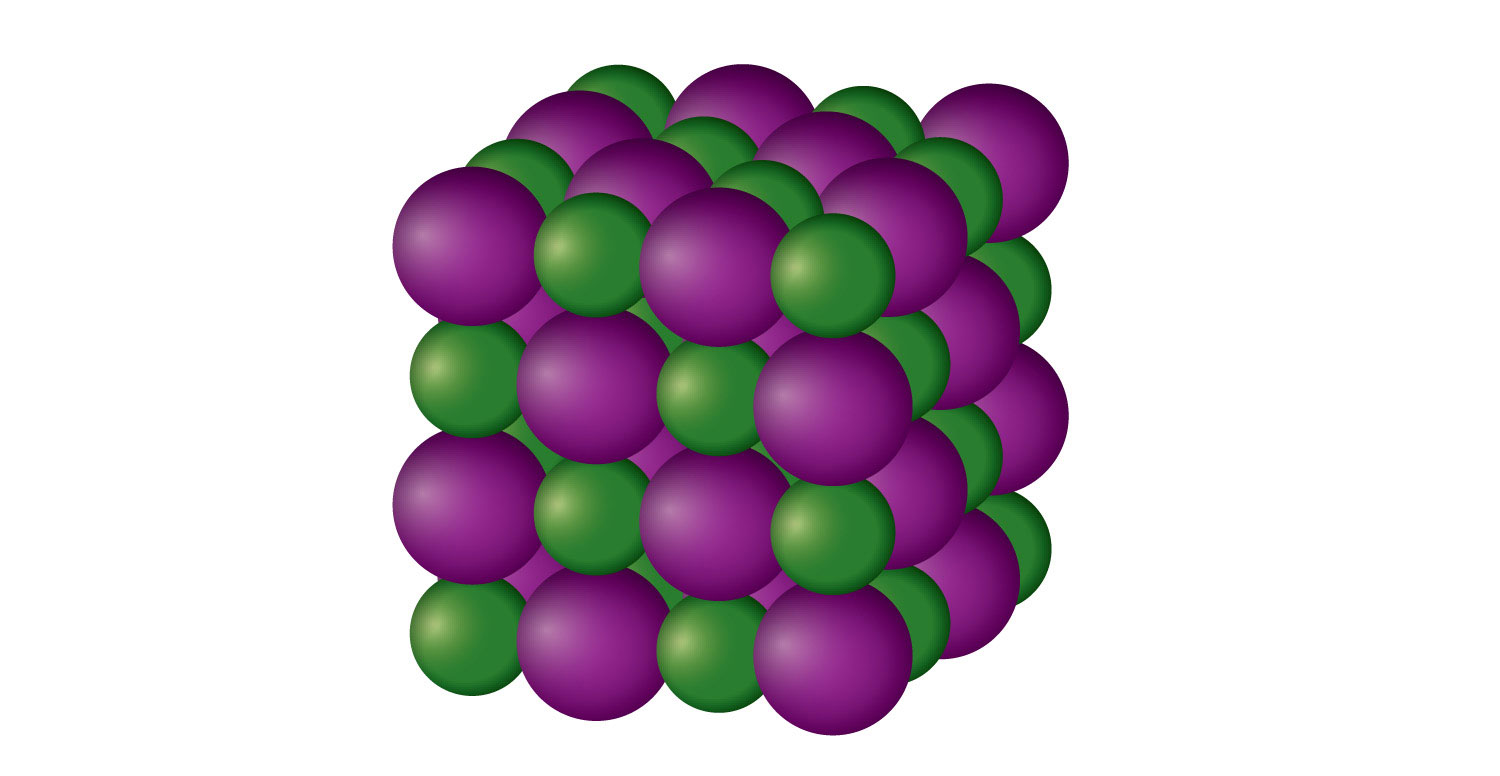
1. Crystalline Solids
Crystalline solids are one of the most common types of solids, characterized by a highly ordered structure and symmetry. These solids consist of atoms, ions, or molecules arranged in a repeating pattern, forming a crystal lattice. This arrangement gives crystalline solids unique physical properties, such as distinct melting points, well-defined shapes, and high levels of hardness.
Characteristics of Crystalline Solids
- Definite geometric shape
- Sharp melting point
- Highly ordered internal structure
- Isotropic or anisotropic properties
Examples of Crystalline Solids
- Salt (Sodium Chloride): Common table salt forms cubic crystals.
- Diamond: A form of carbon with a tetrahedral crystal structure, known for its hardness.
- Quartz: A mineral composed of silicon dioxide, often found in various forms like amethyst and citrine.
2. Amorphous Solids
Amorphous solids differ from crystalline solids in that they lack a long-range order in their atomic arrangement. This irregular structure results in varying physical properties, such as a broad range of melting points and a more flexible nature. Common examples of amorphous solids include glass and certain plastics.
Characteristics of Amorphous Solids
- No definite geometrical shape
- Broad melting range
- Random arrangement of particles
- Typically isotropic properties
Examples of Amorphous Solids
- Glass: A transparent material made by heating silica and other additives.
- Plastic: A synthetic material made from polymers, used in a wide range of applications.
3. Polymeric Solids
Polymeric solids are composed of long chains of repeating molecular units, known as monomers. These materials can exhibit a wide range of mechanical properties, depending on their molecular structure and the degree of polymerization. Polymeric solids can be either crystalline or amorphous, depending on how the polymer chains are arranged.
Characteristics of Polymeric Solids
- High molecular weight
- Can be elastic or rigid
- Varied thermal properties
- Can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable
Examples of Polymeric Solids
- Polyethylene: A widely used plastic, available in various densities.
- Nylon: A synthetic polymer known for its strength and durability, commonly used in fabrics.
4. Composite Solids
Composite solids are materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties. The resulting composite material exhibits enhanced properties, making it suitable for specific applications. This combination can lead to improved strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
Characteristics of Composite Solids
- Enhanced strength-to-weight ratio
- Resistance to corrosion and wear
- Tailored properties for specific applications
- Versatility in design and application
Examples of Composite Solids
- Fiberglass: A composite made of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix.
- Concrete: A mixture of cement, aggregates, and water, used extensively in construction.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored four examples of solids: crystalline solids, amorphous solids, polymeric solids, and composite solids. Each type of solid possesses unique properties and applications that make them essential in various fields, from construction to technology. Understanding these examples allows us to appreciate the diversity of solid materials in our world.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts in the comments section below and explore more articles on this topic to deepen their understanding of solid materials.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again!
Are Horses Ruminants? Understanding Their Unique Digestive System
How Much To Mail A Letter In Canada: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Dog Dewormer Side Effects: What Every Dog Owner Should Know