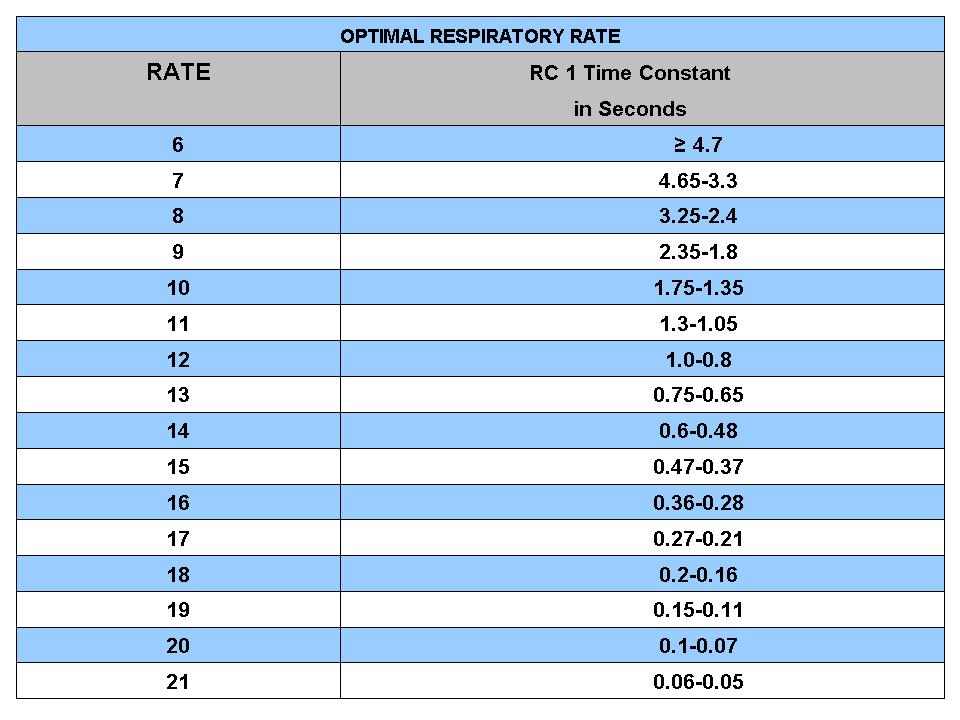
Understanding Respiratory Rate: Importance, Measurement, And Health Implications
Respiratory rate is a crucial indicator of an individual's overall health and well-being. It refers to the number of breaths a person takes per minute and can provide significant insights into respiratory function and metabolic processes. Understanding respiratory rate is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as it can indicate various health conditions and physical states.
In the following sections, we will delve deep into the concept of respiratory rate, its normal ranges, how to measure it accurately, and its implications for health. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a student, or someone simply interested in health, this article will equip you with the necessary knowledge about respiratory rate.
By the end of this article, you will not only understand what respiratory rate is but also why it matters, how to monitor it, and what changes in your respiratory rate might mean for your health. So, let’s take a deep breath and dive into this essential topic!
Table of Contents
- What is Respiratory Rate?
- Normal Respiratory Rate
- How to Measure Respiratory Rate
- Factors Affecting Respiratory Rate
- Respiratory Rate and Health Implications
- Abnormal Respiratory Rate
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Conclusion
What is Respiratory Rate?
Respiratory rate is defined as the number of breaths a person takes in one minute. This vital sign is an essential part of assessing a person's health and is especially important in situations involving respiratory or cardiovascular issues. The respiratory rate is typically measured in breaths per minute (BPM).
In general, the respiratory rate is an indicator of how effectively the body is managing its oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. For healthy adults, a normal respiratory rate typically ranges between 12 to 20 breaths per minute. However, this rate can vary based on various factors, including age, activity level, and health status.
Normal Respiratory Rate
The normal respiratory rate varies significantly with age and physiological conditions. Here is a breakdown of normal respiratory rates by age group:
- Newborns (0-1 month): 30-60 BPM
- Infants (1-12 months): 30-50 BPM
- Children (1-5 years): 20-30 BPM
- Children (6-12 years): 18-25 BPM
- Adults: 12-20 BPM
Monitoring respiratory rate is critical, especially in clinical settings where a patient's condition can change rapidly. Deviations from the normal range may suggest underlying health issues that warrant further investigation.
How to Measure Respiratory Rate
Measuring respiratory rate can be easily done in a clinical setting or at home. Here are the steps to measure your respiratory rate accurately:
- Find a comfortable and quiet place to sit or lie down.
- Place your hand on your chest or abdomen to feel the rise and fall of your breathing.
- Count the number of breaths you take in one minute. A breath is defined as one inhalation and one exhalation.
- For greater accuracy, you may want to measure your respiratory rate for a full minute.
It’s important to remain calm and relaxed while measuring your respiratory rate, as anxiety or physical exertion can artificially elevate your breathing rate.
Factors Affecting Respiratory Rate
Several factors can influence an individual's respiratory rate, including:
- Age: As discussed earlier, respiratory rates differ by age group.
- Physical Activity: Exercise increases the respiratory rate to meet the body’s oxygen demands.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, or anxiety can affect respiratory rates.
- Environmental Factors: High altitudes, pollution, and temperature can influence breathing patterns.
Understanding these factors is essential for interpreting respiratory rate accurately and can provide insight into one’s overall health status.
Respiratory Rate and Health Implications
Respiratory rate can be a significant indicator of health. A normal respiratory rate suggests that the body is managing its oxygen and carbon dioxide levels effectively. Conversely, an abnormal respiratory rate can indicate various health issues:
- Bradypnea: A slower than normal respiratory rate, often below 12 BPM, can indicate conditions such as respiratory depression or neurological disorders.
- Tachypnea: A faster than normal respiratory rate, typically above 20 BPM, can signal issues like fever, anxiety, or respiratory infections.
- Hyperventilation: Rapid breathing can lead to decreased carbon dioxide levels and may indicate anxiety or panic attacks.
Monitoring respiratory rate can help in early detection and management of these conditions.
Abnormal Respiratory Rate
Abnormal respiratory rates can be classified into two main categories:
1. Bradypnea
Bradypnea refers to a slower than normal breathing rate. This may occur in various scenarios, including:
- Drug overdose (especially opioids)
- Severe hypothyroidism
- Sleep apnea
2. Tachypnea
Tachypnea refers to an increased breathing rate. It can be caused by:
- Fever or infection
- Pulmonary embolism
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Both conditions require medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences:
- A respiratory rate that is consistently above or below the normal range.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- Chest pain or tightness.
- Confusion or altered mental status.
Timely intervention can be critical in addressing any serious underlying health issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding respiratory rate is vital for assessing health and well-being. This article has explored the definition of respiratory rate, its normal ranges, how to measure it, factors affecting it, and its implications for health. Monitoring respiratory rate can provide significant insights into an individual's respiratory function and overall health status.
If you found this article helpful, please consider leaving a comment, sharing it with others, or exploring more articles on health topics on our site.
Sources
- American Thoracic Society: www.thoracic.org
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: www.nhlbi.nih.gov
- World Health Organization: www.who.int
Thank you for reading! We hope you will visit our site again for more insightful articles.
What Does The State Level Of Law Enforcement Do?
Exploring The Healing Power Of Music Therapy
Exploring The Life And Legacy Of Souza: A Journey Through Art And Influence
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-normal-respiratory-rate-2248932-v1-5c1abe6846e0fb0001c6284a.png)