Understanding Dot Plots: A Comprehensive Guide To Data Visualization
Dot plots are an essential tool in the realm of data visualization, enabling researchers and analysts to present data clearly and effectively. As we delve into the world of statistics and data representation, understanding how to utilize dot plots can significantly enhance your data analysis skills. This article will explore the definition, construction, advantages, and applications of dot plots, making it a must-read for anyone involved in data-related fields.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover the various aspects of dot plots, including their historical context, the differences between dot plots and other types of visualizations, and their practical applications in various fields such as education, business, and healthcare. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the world of dot plots.
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of dot plots, how to create them, and when to use them effectively. So, let's embark on this journey of data visualization and uncover the power of dot plots!
Table of Contents
- What is a Dot Plot?
- How to Create a Dot Plot
- Advantages of Dot Plots
- Dot Plots vs Other Visualizations
- Applications of Dot Plots
- Examples of Dot Plots
- Common Mistakes in Creating Dot Plots
- Conclusion
What is a Dot Plot?
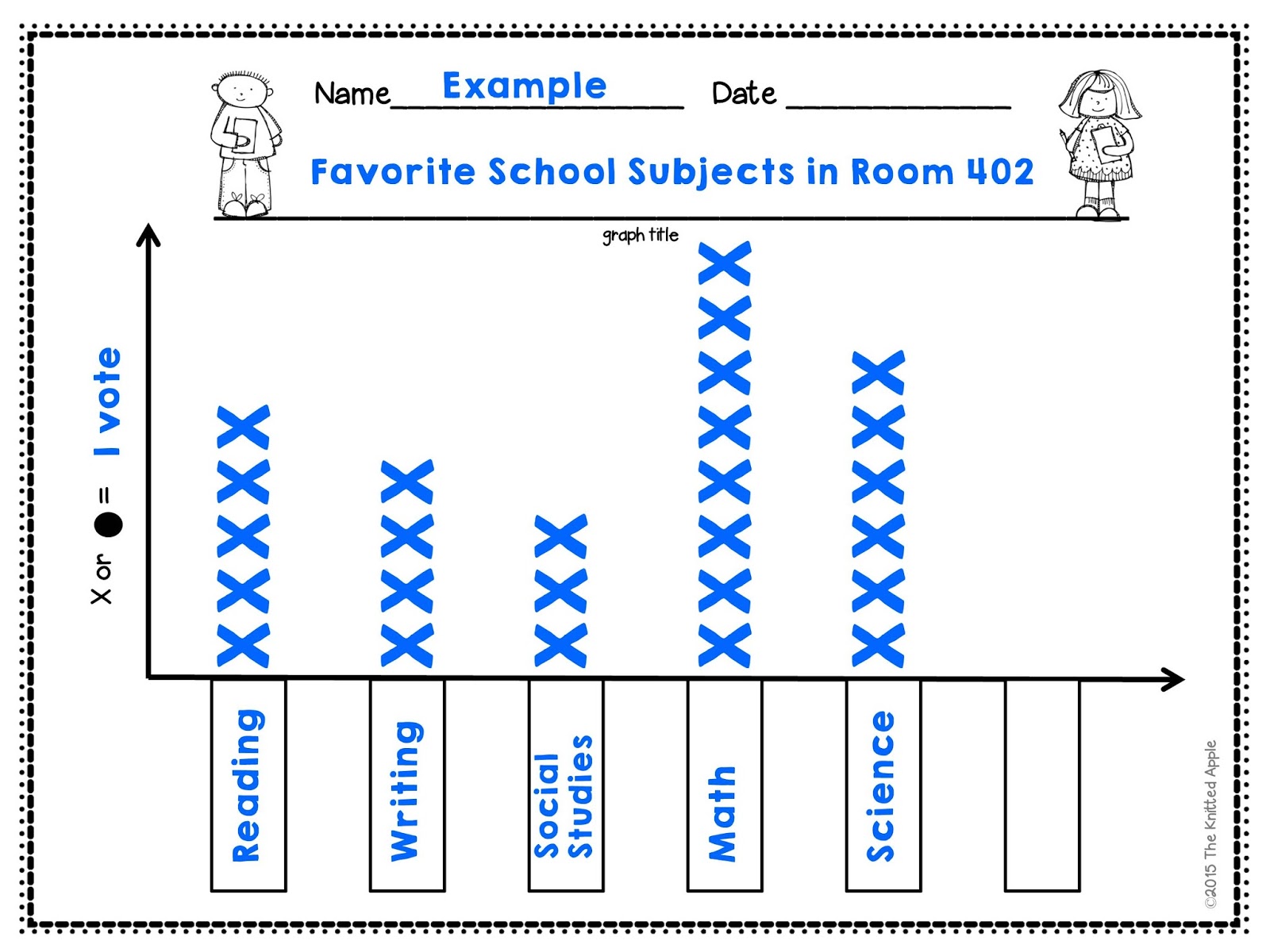
A dot plot is a type of statistical chart that uses dots to represent the frequency of values in a dataset. Each dot represents one data point, and they are typically arranged along a single axis. Dot plots are particularly useful for displaying small to moderate-sized datasets, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the distribution and frequency of the data.
Dot plots can be used for both qualitative and quantitative data, making them versatile tools for data visualization. They are often utilized in educational settings to teach students about data representation and analysis. The simplicity and clarity of dot plots make them an effective choice for communicating data insights to a broad audience.
Key Characteristics of Dot Plots
- Each dot represents a single observation or data point.
- Dots are stacked vertically or horizontally, depending on the orientation of the plot.
- Dot plots can display categorical or numerical data.
- They provide a clear view of the distribution of data points.
How to Create a Dot Plot
Creating a dot plot is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using various tools, including software programs like Excel, R, or Python. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create a dot plot:
Step 1: Gather Your Data
Start by collecting the data you want to visualize. Ensure your data is organized and clearly defined.
Step 2: Choose Your Scale
Determine the scale for your dot plot. This could be a numerical scale or a categorical scale based on your data type.
Step 3: Plot the Dots
For each data point, place a dot on the graph according to its value. If multiple data points share the same value, stack the dots vertically or horizontally.
Step 4: Label Your Axes
Clearly label your axes to indicate what the data represents. Include a title for your dot plot for context.
Step 5: Review and Adjust
Review your dot plot for accuracy and clarity. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure it effectively communicates the data.
Advantages of Dot Plots
Dot plots offer several advantages over other forms of data visualization:
- Simplicity: Their straightforward design makes them easy to interpret.
- Clarity: Dot plots clearly show the distribution of data points, making it easy to identify trends.
- Flexibility: They can be used for both qualitative and quantitative data.
- Space Efficiency: Dot plots take up less space compared to other chart types, making them ideal for presentations.
Dot Plots vs Other Visualizations
While dot plots are useful, it’s important to understand how they compare to other visualization methods:
Dot Plots vs Bar Charts
Bar charts display categorical data using rectangular bars, while dot plots use dots to represent individual data points. Dot plots can show overlapping data more effectively than bar charts.
Dot Plots vs Box Plots
Box plots summarize data using quartiles and medians, providing a quick overview of data distribution. Dot plots, however, display all individual data points, allowing for a more detailed analysis.
Dot Plots vs Histograms
Histograms group data into bins, providing a visual representation of frequency distribution. Dot plots display actual data points, enabling viewers to see individual observations.
Applications of Dot Plots
Dot plots are widely used across various fields, including:
Education
In educational settings, dot plots can be used to teach students about data analysis and visualization. They help students understand concepts like frequency and distribution.
Business
Businesses use dot plots to analyze customer preferences, sales data, and market trends. They can help identify patterns and make informed decisions based on data analysis.
Healthcare
In healthcare, dot plots can visualize patient data, treatment outcomes, and disease prevalence. They assist healthcare professionals in understanding trends and making data-driven decisions.
Examples of Dot Plots
To illustrate the effectiveness of dot plots, here are a few examples:
- A dot plot displaying student test scores, showing the distribution of scores and identifying trends.
- A dot plot visualizing sales data over a specific period, highlighting peak sales days.
- A dot plot representing patient recovery times after treatment, showcasing variations in outcomes.
Common Mistakes in Creating Dot Plots
While creating dot plots, it's essential to avoid common mistakes:
- Overcrowding the plot with too many data points, making it difficult to interpret.
- Using unclear labels or missing axis titles, leading to confusion.
- Neglecting to provide context or a title for the plot.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dot plots are a powerful and effective tool for data visualization. They provide a simple yet informative way to display data, making them ideal for various applications in education, business, and healthcare. Understanding how to create and interpret dot plots can significantly enhance your data analysis skills.
We encourage you to experiment with dot plots in your data analysis projects. If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below or share it with your colleagues. For more insights on data visualization, check out our other articles!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back for more informative content on data science and visualization techniques!
Understanding "What's 30 Of 300": A Comprehensive Guide
Serovital Reviews: The Ultimate Guide To Revitalizing Your Health
Best Margarita Recipe: A Complete Guide To Crafting The Perfect Cocktail