Understanding Power Factor: What Is It And Why Does It Matter?
Power factor is a critical concept in electrical engineering that impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of electrical systems. It quantifies the relationship between real power (the power that actually does the work) and apparent power (the total power flowing in the circuit). Understanding power factor is essential for anyone involved in managing electrical systems, as it plays a significant role in energy consumption, cost efficiency, and system reliability. In this article, we will explore what power factor is, how it is calculated, its significance, and ways to improve it.
As industries and businesses continue to consume more electrical energy, the need for effective power management becomes increasingly important. A low power factor can lead to higher electricity bills, increased losses in the electrical system, and even penalties from utility companies. Therefore, grasping the concept of power factor and its implications can lead to better decision-making and resource management.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of power factor, including its definition, calculation methods, factors affecting it, and strategies for improvement. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of power factor and its importance in electrical systems.
Table of Contents
- What Is Power Factor?
- How Is Power Factor Calculated?
- Importance of Power Factor
- Factors Affecting Power Factor
- Power Factor Correction
- Examples of Power Factor in Various Industries
- Common Misconceptions About Power Factor
- Conclusion
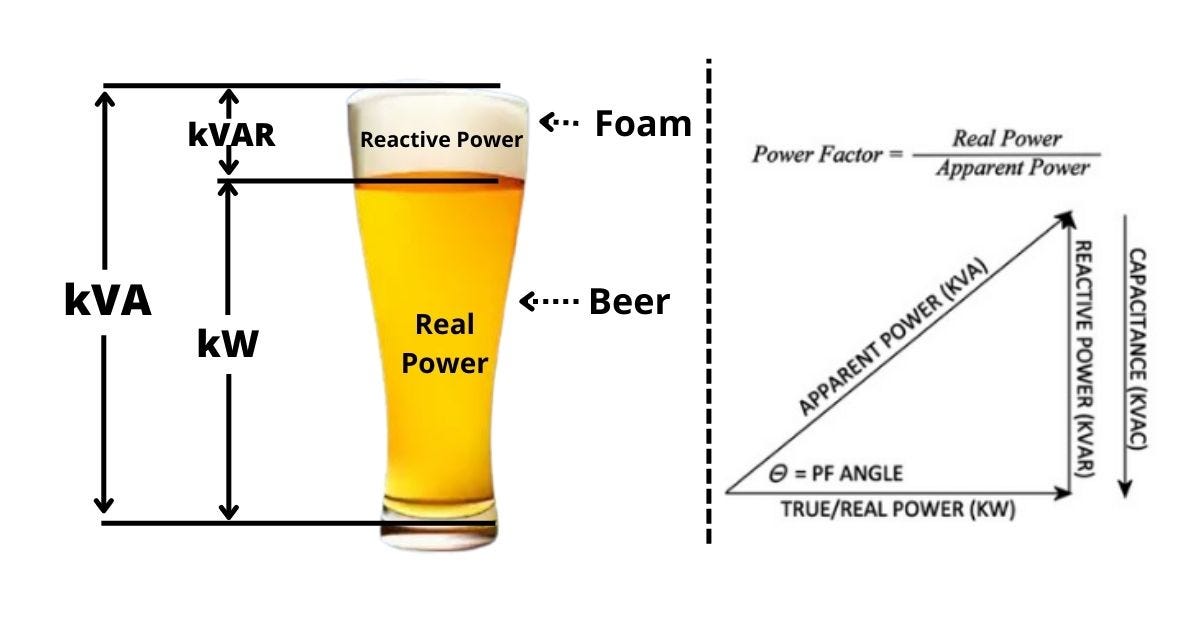
What Is Power Factor?
Power factor is defined as the ratio of real power (measured in watts) to apparent power (measured in volt-amperes). This ratio can range from 0 to 1, with 1 being the ideal scenario where all the power is effectively used. In mathematical terms, power factor (PF) can be expressed as:
PF = Real Power (W) / Apparent Power (VA)
Where:
- Real Power (W): The actual power consumed by the electrical load to perform useful work.
- Apparent Power (VA): The total power flowing in the circuit, which is the product of voltage and current.
A power factor close to 1 indicates efficient utilization of electrical power, while a lower power factor signifies poor efficiency and potential wasted energy.
How Is Power Factor Calculated?
Calculating power factor involves measuring real power and apparent power in a system. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate it:
- Measure the voltage (V) and current (I) flowing through the electrical load.
- Calculate apparent power (S) using the formula: S (VA) = V (Volts) x I (Amperes).
- Measure real power (P) using a wattmeter or power meter.
- Use the power factor formula: PF = P (W) / S (VA).
For example, if the real power consumed is 500 watts and the apparent power is 600 volt-amperes, the power factor would be:
PF = 500 W / 600 VA = 0.833
This value indicates a power factor of 0.833, suggesting that approximately 83.3% of the energy is effectively used.
Importance of Power Factor
Understanding power factor is crucial for several reasons:
- Cost Efficiency: A low power factor can lead to higher energy costs. Utility companies often charge penalties for power factors below a certain threshold.
- System Efficiency: Improving power factor reduces the overall demand for electrical power, leading to less energy waste and enhanced system efficiency.
- Equipment Longevity: A poor power factor can cause overheating and stress on electrical equipment, reducing its lifespan.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many utility providers have regulations regarding acceptable power factor levels, and maintaining a good power factor is essential for compliance.
Factors Affecting Power Factor
Several factors can influence the power factor of a system:
- Load Type: Inductive loads (like motors and transformers) typically have lower power factors, while resistive loads (like heaters) have higher power factors.
- Harmonics: Non-linear loads can introduce harmonics that distort current and reduce power factor.
- Voltage Levels: Variations in voltage can affect the current drawn, impacting the power factor.
- Temperature: Changes in temperature can affect electrical resistance and, consequently, the power factor.
Power Factor Correction
To improve power factor, various correction methods can be implemented:
- Capacitors: Adding capacitors to the system can counteract the effects of inductive loads and improve power factor.
- Synchronous Condensers: These devices can be used to adjust the power factor by supplying reactive power.
- Power Factor Correction Equipment: Specialized equipment is available for businesses to monitor and adjust their power factor automatically.
Examples of Power Factor in Various Industries
Different industries experience varying power factors due to their unique electrical demands:
- Manufacturing: Heavy machinery often results in low power factors, necessitating correction measures.
- Commercial Buildings: HVAC systems can lead to poor power factors, making power factor correction essential for cost savings.
- Data Centers: High-density server environments may also require power factor management to optimize energy consumption.
Common Misconceptions About Power Factor
Several misconceptions about power factor can lead to confusion:
- Power Factor Equals Efficiency: While related, power factor is not a direct measure of efficiency; it is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being used.
- Higher Power Factor Is Always Better: While a power factor close to 1 is ideal, some systems may operate effectively at lower power factors, depending on their design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, power factor is an essential aspect of electrical systems that significantly impacts efficiency, cost, and equipment longevity. By understanding and managing power factor, businesses and industries can optimize their energy usage, reduce costs, and comply with utility regulations. It is crucial for stakeholders to implement power factor correction strategies to enhance overall system performance.
If you found this article informative, feel free to leave a comment, share it with others, or explore more articles on our site for further insights into electrical systems and energy management.
References
- U.S. Department of Energy. (n.d.). Power Factor Correction.
- IEEE Power and Energy Society. (2015). Understanding Power Factor.
- Electrical Engineering Portal. (2023). Power Factor Explained.
Resistance Was Futile: Understanding The Concept And Its Implications
Dungeons And Dragons Character Creation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Doubleist: A Comprehensive Guide